Improvement of the sediment ecosystem following diversion of an intertidal sewage outfall at the Fraser river estuary, Canada, with emphasis on Corophium salmonis (amphipoda)
Primary treated sewage effluent from the city of Vancouver, Canada was deposited directly onto the intertidal ecosystem of Sturgeon bank, Fraser river estuary between 1962 and 1988. In response to the degraded sediment conditions an azoic zone developed near the discharge outfall. Effluent discharges into the intertidal zone were almost completely stopped in 1988 with the construction of a submerged outfall. Our studies, conducted between 1994 and 1996, showed considerable improvement in the environment of the mudflat ecosystem, including increased dissolved oxygen, decreased sediment chlorophyll, decreased organic material in the sediment, reduced heavy metals in surficial sediment and increased grain size. Our data strongly suggest that improvement of sediment conditions near the former sewage outfall was a major factor enabling colonization by C. salmonis.
Simple
- Date (Publication)
- 2001-09
- Cited responsible party
-
Organisation name Individual name Electronic mail address Role DFO
Colin Levings
Principal investigator School of Natural Resources, The Ohio State University
J.L. Arvai
Principal investigator Department of Earth and Ocean Sciences
P.J. Harrison
Principal investigator Department of Zoology, The University of British Columbia
W.E. Neill
Principal investigator
- Presentation form
- Digital document
- Other citation details
-
Marine Pollution Bulletin 44 (2002) 511–519
PII: S00 2 5-3 2 6X(0 1 )0 02 6 4- 8
0025-326X/02/$ - see front matter
- Purpose
-
In this paper we consider the improvement of the ecosystem of Sturgeon bank following the cessation of this stress, focusing on variables such as dissolved oxygen and sediment quality which had been measured in a number of earlier studies during the time when primary treated sewage contaminated the surrounding mudflats.
- Status
- Completed
- Maintenance and update frequency
- Not planned
-
Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Science Keywords v15.9
-
-
Earth Science > Oceans
-
Earth Science > Oceans > Water Quality > Ocean Contaminants
-
-
DFO Areas
-
-
North Pacific Ocean > Fraser River and BC Interior
-
North Pacific Ocean > South Inner Coast(Johnstone Strait, Strait of Georgia, Juan de Fuca, inlets and passages)
-
-
Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Science Keywords v15.9
-
-
Earth Science > Biosphere > Aquatic Ecosystems > Estuarine Habitat
-
Earth Science > Oceans > Marine Sediments > Sedimentation
-
-
DFO Areas
-
-
North Pacific Ocean > Fraser River and BC Interior
-
North Pacific Ocean > South Inner Coast(Johnstone Strait, Strait of Georgia, Juan de Fuca, inlets and passages)
-
-
DFO Areas
-
-
North Pacific Ocean > South Inner Coast(Johnstone Strait, Strait of Georgia, Juan de Fuca, inlets and passages)
-
-
Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Science Keywords v15.9
-
-
Earth Science > Biological Classification > Animals/Invertebrates > Arthropods > Crustaceans > Amphipods
-
Earth Science > Biosphere > Aquatic Ecosystems > Estuarine Habitat
-
Earth Science > Biosphere > Ecological Dynamics > Community Dynamics > Indicator Species
-
Earth Science > Human Dimensions > Environmental Impacts > Sewage
-
-
DFO Areas
-
-
North Pacific Ocean > Fraser River and BC Interior
-
- Use limitation
-
Copyright 2002 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved.
- Language
-
English
- Character set
- UTF8
- Topic category
-
- Oceans
- Environment
- Environment description
-
14 KB
- Description
-
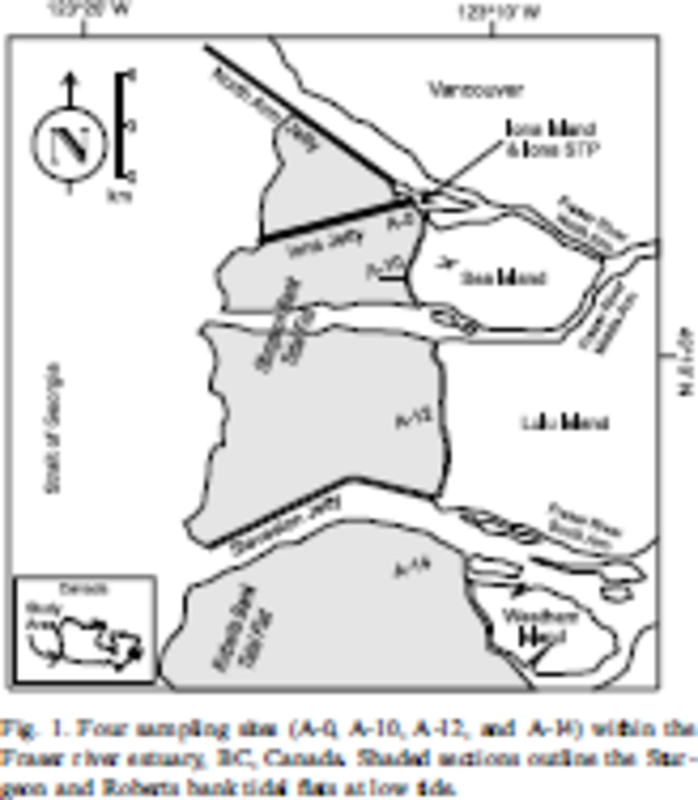
Four sampling sites within the Fraser river estuary, BC, Canada.
))
- Begin
- 1994-05-10
- End
- 1996-11
- Supplemental Information
-
Primary treated sewage effluent from the city of Vancouver, Canada was deposited directly onto the intertidal ecosystem of Sturgeon bank, Fraser river estuary between 1962 and 1988. In response to the degraded sediment conditions an azoic zone developed near the discharge outfall. Effluent discharges into the intertidal zone were almost completely stopped in 1988 with the construction of a submerged outfall. Our studies, conducted between 1994 and 1996, showed considerable improvement in the environment of the mudflat ecosystem, including increased dissolved oxygen, decreased sediment chlorophyll, decreased organic material in the sediment, reduced heavy metals in surficial sediment and increased grain size. The amphipod Corophium salmonis, important in the food web for juvenile salmon and other fish species, recolonized the previously azoic location. At reference stations, C. salmonis density was similar to that observed in previous surveys two decades earlier. Our data strongly suggest that improvement of sediment conditions near the former sewage outfall was a major factor enabling colonization by C. salmonis.
- Distribution format
-
Name Version electronic
none
- Distributor contact
-
Organisation name Individual name Electronic mail address Role Pacific Salmon Foundation
Isobel Pearsall
Distributor
- OnLine resource
-
Protocol Linkage Name WWW:LINK-1.0-http--link
https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/science/data-donnees/index-eng.html DFO Science website
WWW:DOWNLOAD-1.0-http--download
https://soggy2.zoology.ubc.ca/geonetwork/srv/api/records/09155311-8f2f-4d7c-95a0-6f5f235f0e31/attachments/09155311-8f2f-4d7c-95a0-6f5f235f0e31.pdf 09155311-8f2f-4d7c-95a0-6f5f235f0e31.pdf WWW:DOWNLOAD-1.0-http--download
https://soggy2.zoology.ubc.ca/geonetwork/srv/api/records/09155311-8f2f-4d7c-95a0-6f5f235f0e31/attachments/09155311-8f2f-4d7c-95a0-6f5f235f0e31.xlsx 09155311-8f2f-4d7c-95a0-6f5f235f0e31.xlsx
- Hierarchy level
- Dataset
- Statement
-
Levings produced paper copy. Fraser scanned with Fujitsu Scansnap s1500 (ABBY Finereader OCR software). Data was extracted through Adobe Reader conversion and manual entry into MS Excel.
Metadata
- File identifier
- 09155311-8f2f-4d7c-95a0-6f5f235f0e31 XML
- Metadata language
-
eng
- Character set
- UTF8
- Hierarchy level
- Dataset
- Date stamp
- 2023-12-19T00:17:59.346Z
- Metadata standard name
-
North American Profile of ISO19115:2003 - Geographic information - Metadata
- Metadata standard version
-
NAP - CAN/CGSB-171.100-2009
- Metadata author
-
Organisation name Individual name Electronic mail address Role Pacific Salmon Foundation
Sarah Fraser
Author
- Other language
-
Language Character encoding French UTF8 English UTF8
Overviews
Spatial extent
))
Provided by
